Executive compensation is composed of salary, bonuses, stock options, and other company benefits. Staggering figures like the CEO-to-worker pay ratio of 354:1 (in 2012) have brought executive compensation under some scrutiny in the United States. Other provisions like the ‘say on pay’ provision of the Dodd-Frank Act have brought executive compensation to the forethought of many shareholders’ minds.
Let’s start with a quick exercise. Which of the following CEOs had the highest base salary for the year 2012?
A. Larry Page (Google)
B. Alex Gorsky (Johnson & Johnson)
C. W. James McNerney, Jr. (Boeing)
D. C. Douglas Mcmillon (Walmart)
I’m not sure who you guessed (the answer is C), but we can quickly find out answers to questions like this using several library databases. A number of publications provide lists of the top paid CEOs, like Forbes’ list of America’s Highest Paid Chief Executives. Lists are helpful, but you may want to search by company or executive or create a time series of data.
LexisNexis Academic allows you to search within the Morningstar US Executive Compensation database. This source provides information on salaries, cash compensation, option grants, other stock-related compensation and auditor fees for U.S. public company directors and officers. Data comes from the Form 10-K or Annual Meeting Proxy Statements. The coverage is the current edition (i.e. FY 2013) and does not include historical data. Click Search by Content Type and select Company Profiles. Under the Advanced Options area select the source. Then search by company name (e.g. Apple Inc.) or by executive (e.g. Larry Page). This database is helpful if you are searching for a single company or executive.
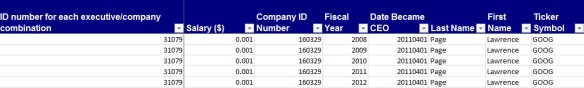
Standard & Poor’s Execucomp database is available through WRDS (for Wharton account holders). Go to COMPUSTAT and select Execucomp. This database covers 2,872 companies, both listed and unlisted, with data for up to 9 executives, although most companies only report 5. Similar to the Morningstar database, this data is collected from each company’s annual proxy (DEF14A SEC form). With data back to 1992 and numerous fields to select from (e.g. EIP_UNEARN_NUM — Equity Incentive Plan–Number of Unearned Sha), this is a good database to use to build a time series. Below is an example of Google’s data for the past 5 years, with only Larry Page’s salary shown.
GMI Ratings (formerly Corporate Library), is another database available through WRDS, which also covers executive compensation. Data goes back to 2001 and primarily covers:
• Corporate Board Structure and Independence
• Director Positions and Committee Assignments
• Executive Compensation
• Director Compensation
• Audit Fees
• Takeover Defenses
• Corporate Ownership
Bloomberg, available in the Lippincott Library and Huntsman Hall, provides compensation data as well. For an individual company, use the command FA EXEC. For example, if you wanted executive compensation for Google, type the following into the command line:
GOOG <EQUITY> FA EXEC <GO>
Bloomberg also provides some aggregated data in the Corporate Governance Industry Dashboard. Use the command BI CGOVG. You can select one of the pre-selected peer groups like the Russell 1000 or click on “Select Companies” to build your own screen.
For additional sources for CEO salaries see our Business FAQ on Executive Compensation.